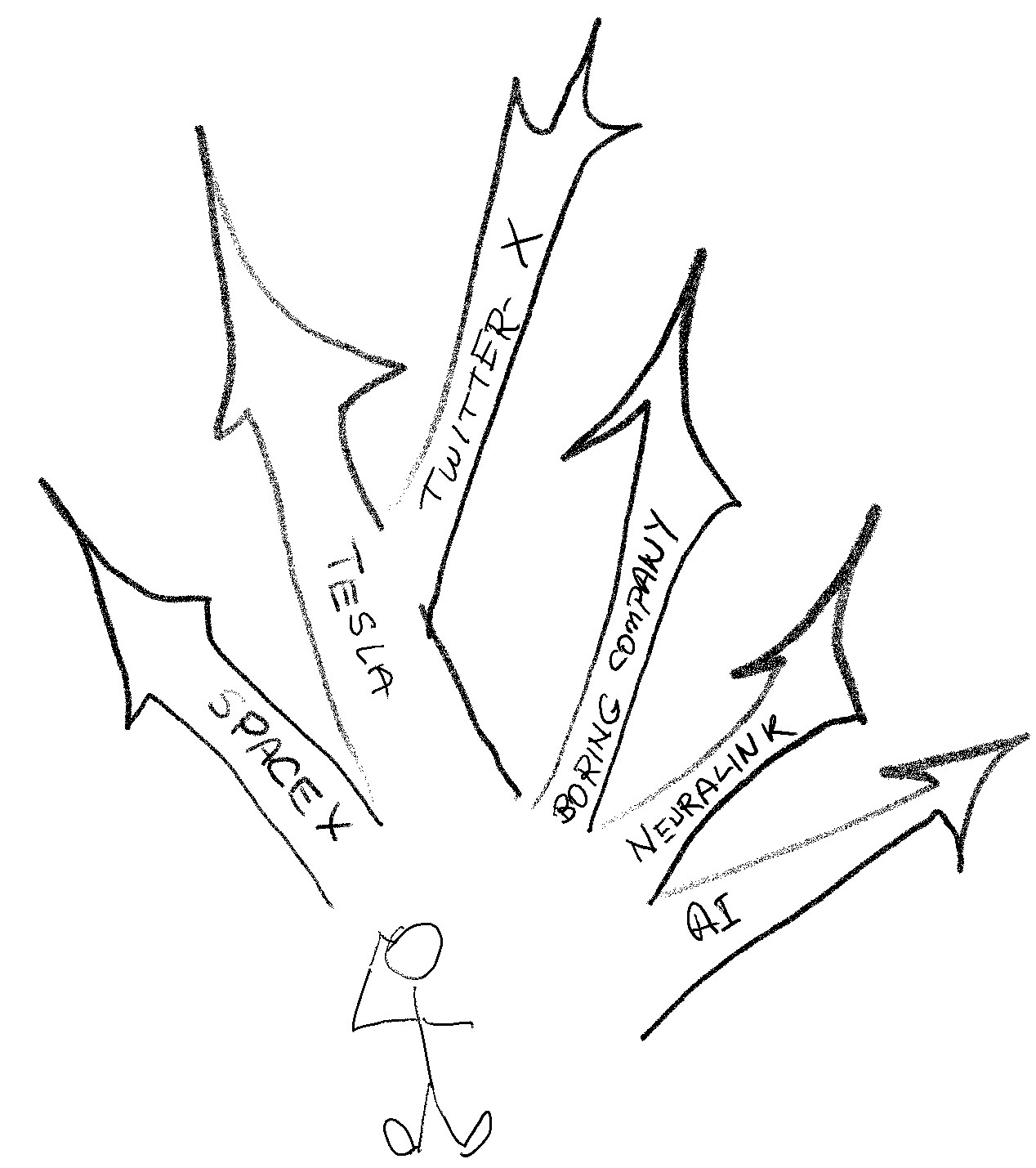
Elon Musk: The Spaceman
While it is Tesla that made Elon Musk the richest man of the globe, I think his most significant impact will be his work in transforming the space industry.
Please subscribe; please share. This blog will always be free but worthy reading.
-+-+-+-+
Key Points
🚘 Elon Musk, known as the richest person in the world by Forbes, owes much of his financial success to Tesla, but it's his revolutionary work in the space industry with SpaceX that is likely to be his most lasting impact.
🚀 SpaceX became successful by challenging the traditional cost-plus contracts in the aerospace industry.
🛰️ Despite initial setbacks and near bankruptcy, SpaceX achieved the first successful orbit with the Falcon 1 rocket and subsequently secured a significant NASA contract for resupply missions to the International Space Station.
🌓 SpaceX's achievements include the first reusable rocket landing, Starlink satellite internet service, and being chosen by NASA to develop the Starship for future Moon missions.
👏 Musk's SpaceX has reinvigorated space exploration, making significant strides towards the goal of Mars colonization and marking a new era of privately-led space travel.
Forbes says Elon Musk is the richest person of the world
While it is probably Tesla that made Elon Musk the richest man of the globe, I think his most significant impact will be his work in transforming the space industry.
-+-+-+-+
Many people made it from rags to riches. But he is the only one I know who started from zero, made his first fortune; then instead of sitting back and taking it easy, risked it all and won and multiplied his wealth. Then you thought after the second time lucky he would sit back and start enjoying different things in life but he split his fortune in five and risked it all again.
Let us start from the beginning. Elon was one of the three kids born to Errol and Maye Musk in South Africa. He had one elder brother Kimbal and a younger sister, Tosca. Errol and Maye separated when Elon was five years old. Elon grew up partly with his mum and partly with his dad. They were a middle class family. In 1989, Elon, his siblings and the mother migrated to Canada, where they all had to work hard just to make ends meet. There was little money for luxuries. Elon started tertiary education at Queen’s in Canada but then switched to the University of Pennsylvania on a $14,000 scholarship. He did a double degree in Physics and Business but was very interested in computing since he was eleven.1.
Then he enrolled to a do Masters on Material Science at Stanford University. Musk had a life vision which he would repeat like a mantra around that time: There are three things that will truly affect humanity: the internet, the sustainable energy, and space travel.
Internet was exploding then and this is what he started with.
Asking for a deferral from Stanford (he never went back), he started an internet company with his brother Kimbal. Their product was Zip2, a searchable directory of businesses online combined with map software that would give users directions. , They built it up in less than four years and sold it to Compaq for $307m in 19992. The VC investors took their share and the brothers ended up with $37m between them.
For someone who started as a poor migrant, this was an unimaginable bounty. A less ambitious man would probably retire and live comfortably off that sum. Musk did not. He spent some of it (with his brother he gave $300,000 to their father and $1m to their mother; he bought a McLaren F1 sports car3 for another $1m) and the rest he put into a new company X.com4.
After merging with their competitor, Peter Thiel, X became PayPal5 , which was purchased by eBay for $1.5 billions in 2002. Musk walked away with $250 millions. His PayPal mates have been living on the proceeds of their share of the bounty since then. But not Musk. His only dilemma was that he had too many things he wanted to do and it was hard to decide.
At the end, he decided to do them all.
-+-+-+-+
Mission to Mars -- SpaceX
In 2000, Musk caught malaria during a trip to South Africa. He almost died because he was not diagnosed early enough6. The next year, he decided that it was time to do something in space. James Cameron convinced him that humans were doomed unless they colonized other planets and Mars was the only feasible option.
Elon first tried to start using second hand rockets. The only people who had spare rockets those days were the Russians. Musk went to Moscow twice chasing after ex Soviet rockets but the Russians thought he was a lunatic and did not take him seriously. He bid for two Dnepr rockets, which were old missiles. Russians first said $18m for the two but then they took it up to $21m for one rocket.
Musk was upset but it turned out for the better at the end. The Russian snub pushed him to conceive one of the most audacious ventures of our times: privately building rockets that could launch satellites and then humans into orbit and eventually send them to Mars and beyond. The advantage of this scheme was that it made the Mission to Mars a staged project where Musk had the opportunity to recoup his costs at every stage. This was typical. Like one of his PayPal mates Reid Hoffman said, "Elon starts with a mission and later finds a way to backfill in order to make it work financially. That’s what makes him a force of nature.”
-+-+-+-+
SpaceX
So Elon Musk forms the company SpaceX to build rockets. Its first product Falcon 1 was designed and built using Elon's own funds. At that time, the space business was a sheltered industry with jobs allocated between a limited list of companies on cost plus contracts from NASA. A cost plus contract meant that the companies did not commit to a fixed price. They kept a cost record which they sent to NASA and NASA reimbursed them plus a predetermined profit margin. In a cost-plus contract, there is not much incentive for the company to cut down the costs. Therefore, everything costs a lot more than it should. When I used to work as a consultant, we loved cost plus contracts.
Musk challenged this scheme. In 2004, NASA awarded a $227m contract to a rival rocket company Kistler Aerospace without competitive bidding. The contract was for rockets to take supplies to the International Space Station (ISS). Musk thought Space X could do better. He sued NASA and he won. The court ordered NASA to reopen the contract to competitive bidding and SpaceX won a large part of it.
To break down the oligopoly of the established companies such as Boeing and Lockheed and others, Musk energetically lobbied against cost plus contracting. He testified before a Senate Committee. “Boeing and Lockheed just want their cost-plus gravy trains,” he said. “They have an incentive never to finish. If you never finish a cost-plus contract, then you suckle on the tit of the government forever.” Musk knew that the established companies could not compete against SpaceX on cost. Therefore, he pushed for the alternative in which private companies would risk its own capital and would be paid only if and when it delivered on certain milestones. The government accepted this approach and in only a number of years SpaceX was able to get ahead of all competition in rocket business.
But it was not easy. A string of bad decisions and bad luck almost killed the company and bankrupted Elon Musk.
-+-+-+-+
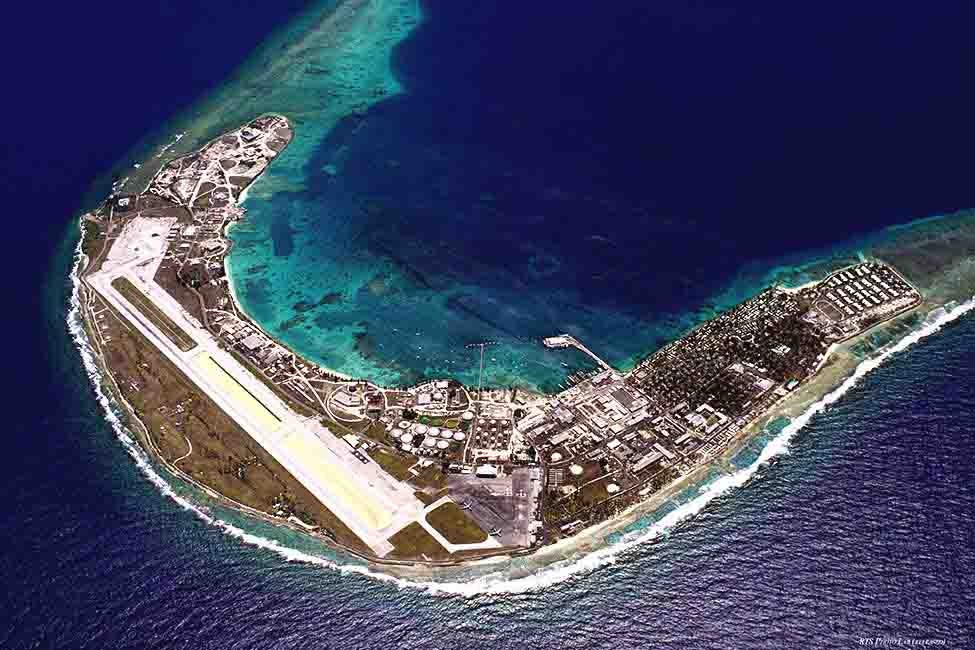
Launch Site at Kwaj
SpaceX scored a $6 million deal in 2003 to launch a communications satellite for Malaysia. Musk wanted to use Air Force's Vandenberg site in California but could not get it. They decided to use the Kwaj atoll site near Marshall Islands. The place was 8000 kilometers west of Los Angeles in the middle of the Pacific Ocean. Musk now says that it was a bad decision. They should have waited for Vanderberg.
On the other hand, it can be said that the four years the team spent on Kwaj atoll was a bonding experience. All is well that ends well.
In Kwaj, they tried their first rocket Falcon 1 three times with no success. The first failed on launch because of a corroded nut on the fuel line. The corrosion was most likely due to the salty air of the site. The second time it failed five minutes into the air losing spin control due to sloshing of the fuel. Baffles in the tank could have prevented it with the benefit of hindsight. The third launch attempt also failed with the separated booster travelling the wrong way and hitting the payload.
After three launch failures, SpaceX had no money left. Musk's other venture Tesla also was doing badly partly due to the effects of Global Financial Crisis. Musk was bankrupt. His old PayPal partners came to help. Peter Thiel put in $20m.
On 28 September 2008, the SpaceX team tried again. This was the fourth attempt and this time everything went perfectly and the payload was released to its intended orbit.
Falcon 1 was the first privately built rocket to reach orbit. Compared to the space division of Boeing that had 50000 employees, SpaceX only had 500. These five hundred staff designed and built the rocket. Little was outsourced. And the funding was largely out of Musk’s pocket.
The successful launch made SpaceX a credible company overnight. After the Space Shuttle, NASA was searching for a new way to send crew and cargo to the International Space Station (ISS). On 22 December, three months after the successful Falcon 1 launch, NASA awarded $1.6 billion to SpaceX for 12 round trips to ISS.
-+-+-+-+
SpaceX given a Cape Kennedy test site
SpaceX became part of the US Space industry landscape. For example, they got a test site in Cape Kennedy, Florida. They did not have to travel half way around the world to Kwaj for each launch any more.
The ISS payload was heavier. Musk wanted to build a new engine but SpaceX staff managed to convince him to use the proven Falcon 1 engine but more of it. The new rocket had nine of the Falcon 1 engines and was called Falcon 9.
Falcon 9 launched successfully in the first attempt. A good sign for the future of SpaceX. In fact, from that point on, SpaceX moved from success to success. Occasional failures did not detract the company from its main mission: travelling to Mars. I suggest you read Isaacson’s book for the detailed story.
Some milestones
21 December 2015 - After taking its payload to the orbital velocity, the Falcon 9 booster comes back to Cape Kennedy and lands back on its launch pad. First demonstration of a reusable rocket.
May 2019 - Falcon 9 releases Starlink satellites into the orbit. Musk now owned his own internet. By mid-2021, 2000 Starlink satellites are launched with the space-based internet becoming available in 14 countries.
2021 - NASA picks SpaceX Starhip to take astronauts and cargo to Moon and back for the second phase of its lunar project. I wrote about it a few months ago.
In a nutshell, Elon Musk and SpaceX made space travel feasible again. Fifty years after the last manned mission to the Moon (Apollo 17, December 1972), the humanity is planning to go the Moon again and this time possibly to stay there.
-+-+-+-+
Short Takes
Infant Mortality in USA
NVSS Vital Statistic Rapid Release Report No 33, November 2023
The infant mortality rate for the United States rose 3% from 2021 to 2022, the first year-to-year increase in the rate since 2001 to 2002. From 2002 to 2021, the infant mortality rate had declined 22%. Interestingly, the report says that the mortality rate increased significantly only for male infants. This could be a statistical outlier or it could be an indication of deterioration in US health services or something else. It is a trend to watch for in future years.
-+-+-+-+
You Tube video of the week
My recommended video this week is the chat between the British PM Rishi Sunak and Elon Musk:
I recommend this video because I think we need some sanity in the AI debate. Quite a few people are dead scared of the coming AI revolution and their fright is being fed by two sources:
Popular sociologists like Harari (but not only him), who probably believe AI scare is a good horse to back for maintaining their global exposure. They probably also understand that a competent AI can author aphorisms as well as they can, if not better.
The bosses of the companies who are currently leading the technology such as OpenAI, Google, etc want regulations because this way they can control and suppress the technology development by new companies before they become competition.
Elon Musk is very optimistic about a future with AI but understands that there need to be safeguards, which he believes are possible. I was interested that he referred to late Iain Banks as an author who had depicted a future of abundance made possible by advanced AI. Most people would pick Gibson or Stephenson on AI futures but I agree with Musk’s reference. It is not a reference to the technology but what should be possible when we have a working techology.
-+-+-+-+
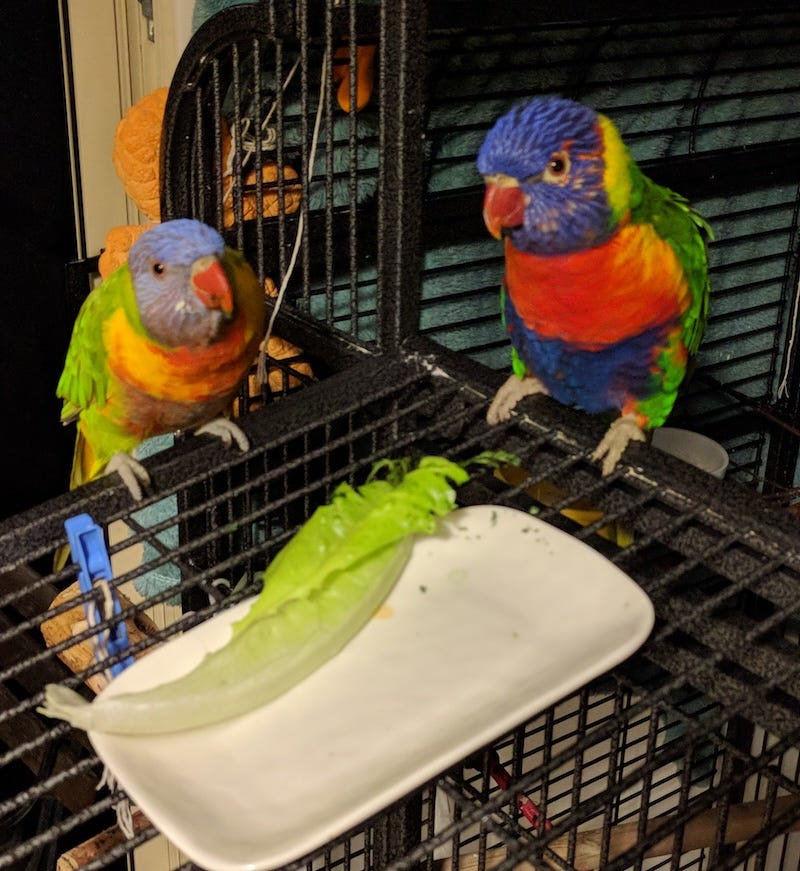
Pascal Hagi
I keep my office door closed during the day, locking Pascal and Hagi outside in the garden. Otherwise, they try to join me on the keyboard and play all kinds of havoc. I open the door when it starts getting dark. They quickly fly in, Pascal first and then Hagi follows. I feed them a leaf of lettuce as afternoon snack. Their main feed is inside the cage but we like them to have a balanced diet eating their greens🥬🥬👍.
It is interesting that they only eat it if I serve it on a plate as above. If I leave the leaf on the rack, Pascal picks it up and throws it down and says “Ooops, sorry”. Really.
Pascal takes big bites but Hagi takes small bites from the leaf area between the veins.
-+-+-+-+
Diary
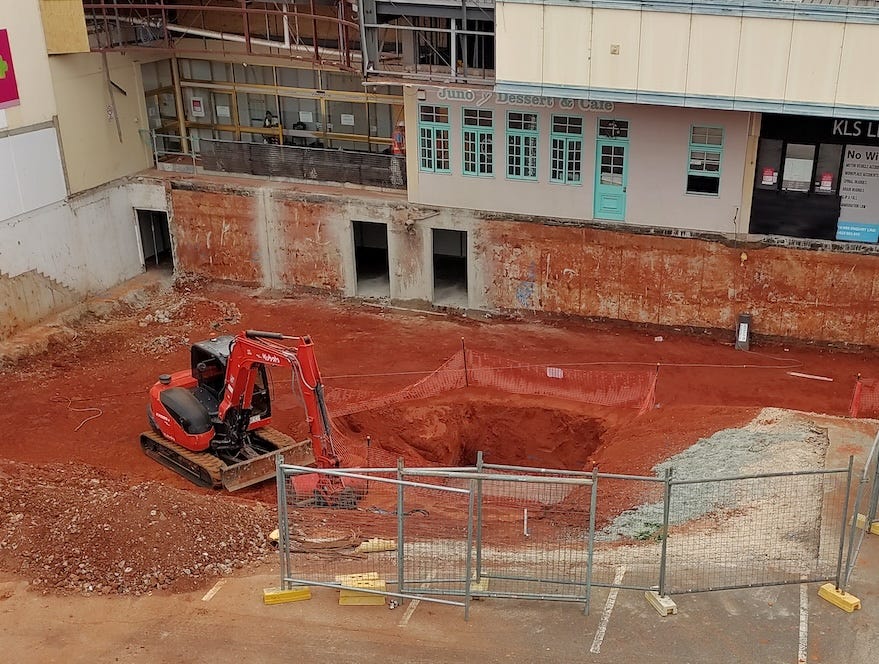
In the Sunny Park shopping centre, they cancelled part of the car park and dug a hole in the ground. I was interested in the color of the soil.
The red color probably comes from iron oxides. I asked ChatGPT for red soil coloring. It said that the main reason is the presence of iron oxides. The oxidation is enhanced in warm moist climates and as a result red soils are more common in tropics or subtropics. Also, the well-drained soils are more likely to be red because flow of water and air encourages oxidation. Finally, older soils will have more intense red coloring because they would be exposed to air and water longer. All of these apply in this instance. My hometown in Turkey, Eskisehir, had a suburb named Kiziltoprak, literally meaning red soil, but I do not remember how red the soil really was.
-+-+-+-+
Zika Statistics
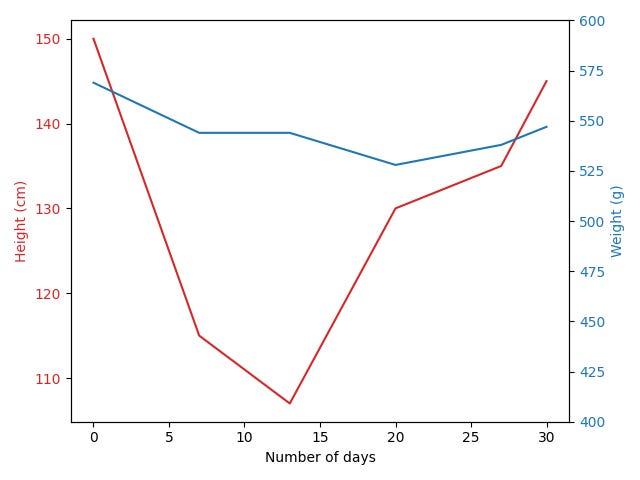
Regular readers from past posts will remember how I am monitoring the height of the sourdough I buy from Zika’s pastries to see if I could see a pattern to the baker making new sourdough culture. I decided to start presenting the data as a graph7:
The date for Day 0 is 4 October 2023.
-+-+-+-+
He was introduced to computers at the age of eleven. He buys a Commodore VIC 20 with the money he saves from his jobs
.
The year is 1983, I guess. In the same year, I bought a Sharp computer similar to it, but I remember the VIC 20 as an alternative. Programs at that time came on audio cassettes. You could write your own program using BASIC (Sharp also had PASCAL). There was no internet yet. I also learned from the book that he loved the computer game, Sid Meir’s Civilisation. I discovered that game in 1993 and also was addicted to it for a long time. Unlike me, Musk then switched to Warcraft and is still a computer game tragic.
This was lucky because the internet bubble burst in 2000 and it is impossible to predict what the value could have been after the bubble burst
He was a petrolhead. While at Penn, he owned a 20-year old BMW 300i. He liked taking it apart and putting it together again. It was a 4-speed car but he took the gearbox out and replaced it with a new 5-speed transmission. He liked fiddling with things
Yes, this is where Twitter's new name comes from
Musk vehemently tried to keep the name X.COM and also wanted to continue his original vision for the company, a truly digital bank. But Thiel and investors disagreed and Musk was ousted from the management although he kept his equity. This probably was a good thing considering the money he made out of this venture
A similar incident happened to a friend of mine who picked malaria while working in Sudan and could not be diagnosed at first in Turkey. He was lucky to be seen by Professor Esin Davudoğlu Şenol who made the right diagnosis and my friend was saved.
I asked VS Code copilot to write the function that creates this plot. It had no problem with it. I copy here for Python users who are interested to learn how AI can help with coding. I could easily do it myself but it would probably take me at least one hour. This took five minutes.
# The function zikaplot(date, height, weight) plots weigt and height versus the number of days
# The argument date is an array of dates in the format of 'dd-mm-yyyy'
# Normalise weight and height to the first value
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import datetime
from datetime import datetime
def zikaplot(date, height, weight):
# Convert date strings to datetime objects
dates = [datetime.strptime(d, '%d/%m/%y') for d in date]
# Calculate number of days since the first date
days = [(d - dates[0]).days for d in dates]
# Normalize height and weight to the first value
norm_height = [h / height[0] for h in height]
norm_weight = [w / weight[0] for w in weight]
# Plot height and weight versus number of days
plt.plot(days, norm_height, label='Height')
plt.plot(days, norm_weight, label='Weight')
plt.xlabel('Number of days')
plt.ylabel('Normalized value')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
date=["4/10/23", "11/10/23", "17/10/23", "24/10/23", "31/10/23", "3/11/23"]
height=[150, 115, 107, 130, 135,145]
weight=[569, 544, 544, 528, 538,547]
zikaplot(date, height, weight)
# Now plot height and weight on different axes
def zikaplot2(date, height, weight):
# Convert date strings to datetime objects
dates = [datetime.strptime(d, '%d/%m/%y') for d in date]
# Calculate number of days since the first date
days = [(d - dates[0]).days for d in dates]
# Plot height and weight versus number of days
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots()
ax1.set_xlabel('Number of days')
ax1.set_ylabel('Height (cm)', color='tab:red')
ax1.plot(days, height, color='tab:red')
ax1.tick_params(axis='y', labelcolor='tab:red')
ax2 = ax1.twinx() # instantiate a second axes that shares the same x-axis
ax2.set_ylabel('Weight (g)', color='tab:blue') # we already handled the x-label with ax1
ax2.plot(days, weight, color='tab:blue')
ax2.tick_params(axis='y', labelcolor='tab:blue')
ax2.set_ylim(400, 600)
fig.tight_layout() # otherwise the right y-label is slightly clipped
plt.show()
zikaplot2(date, height, weight)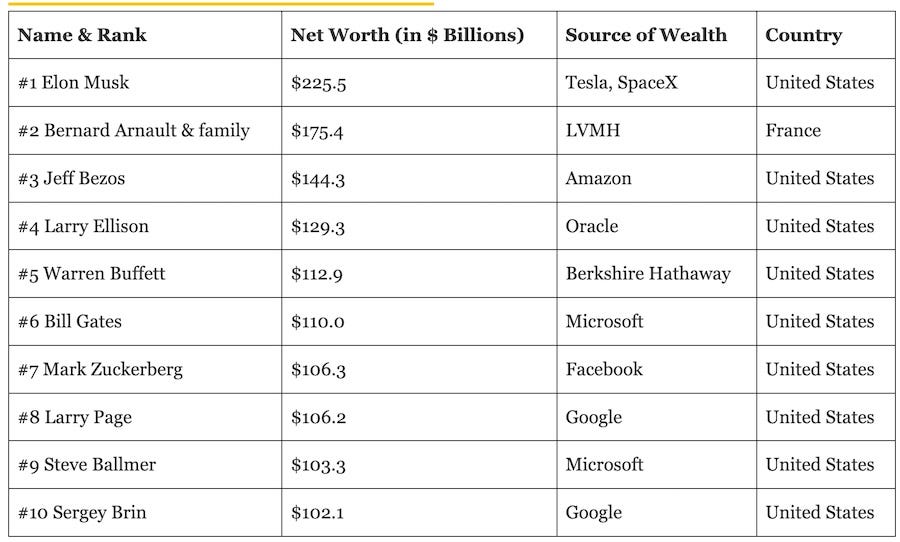






I am not sure what he would propose with the present technology but he probably would be looking into using AI as personalised tutors. In fact, I suspect in less then ten years time AI tutors will be good enough to even be certified as gatekeepers, i.e. assessors or providers of qualifications. Then, there would be little need for universities as we know now.
How would Elon rework the current system for funding university research? How does the incentive structure there compare to cost-plus do you think?